
 Clinical specialty
Clinical specialty
WALANT is a tumescent anesthesia that involves injecting a relatively large volume of low-concentration, bicarbonate-buffered, Lidocaine with Epinephrine into the subcutaneous tissue of the surgical site. In our example, the ultrasound-guided tumescent anesthesia is combined with a median nerve hydrodissection for carpal tunnel release surgery.
Lidocaine and Epinephrine avoid the need of a tourniquet and provide regional anesthesia, which lasts up to 4 or 5 hours. This method optimizes patient comfort, safety, and the operating time spent performing anesthesia in the operating room.
In the following example, a tumescent anesthesia is associated with the hydrodissection of a median nerve. Both of them will be performed 20 to 25 minutes before the surgical decompression of the median nerve.
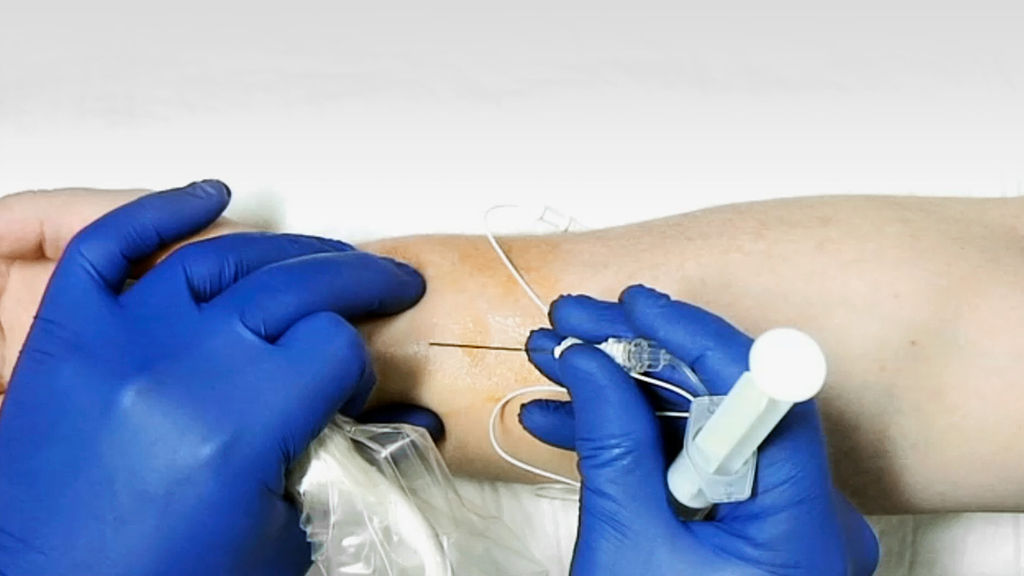
The initial puncture point is located directly above the median nerve proximal to the wrist crease.
We start by defining the initial puncture point, directly above the median nerve proximal to the wrist crease. The injection is performed slowly over five-minute intervals with a 25-gauge block needle. 10 ml of solution is slowly injected into the wrist subcutaneously. Another 10 ml is injected into the palm.
By slowly injecting a large volume and making sure there is visible or palpable local anesthesia – and also slowly advancing the needle, the patient feels very little pain. Make sure that the needle tip never gets ahead of the advancing wheel of local anesthesia.
The goal is to get at least five to ten millimeters of white tumescent tissue at our site of any incision and surgical area..
The ultrasound guided procedure may be performed in-plane or out of plane.
After injection, the injected skin is tumescent and white linked to vasoconstriction. After the tumescent anesthesia, the needle is withdrawn and redirected deeper to the median nerve. The median nerve is hydrodissected avoiding direct needle nerve contact.
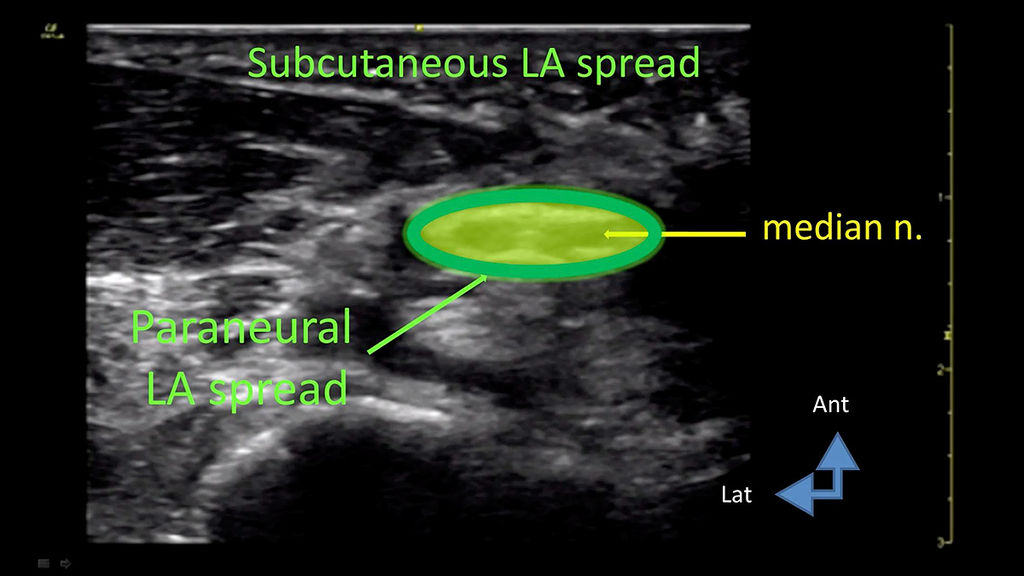
Perfect work: the local anesthetics have spread precisely in the subcutaneous tissue and along the median nerve.
A total volume of 20 ml of local anesthetics was injected. – We see the local anesthetics spreading in the subcutaneous tissue and along the median nerve.
Ultrasound-guided tumescent anesthesia optimizes patient comfort, safety, and the operating time.
Tumescent anesthesia has several important advantages for patients and physicians. It’s comfortable, tourniquet free, and the awake patient cooperates with true active movement during the surgery.
The patient understands the result and knows it will work after the surgery.